- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
An integrative taxonomy approach evaluates the limits of the widespread tarantula Plesiopelma longisternale (Araneae: Mygalomorphae: Theraphosidae) and reveals a new species from Argentina
Posted by
Luis A. Roque
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
An integrative taxonomy approach evaluates the limits of the widespread tarantula Plesiopelma longisternale (Araneae: Mygalomorphae: Theraphosidae) and reveals a new species from Argentina
Abstract
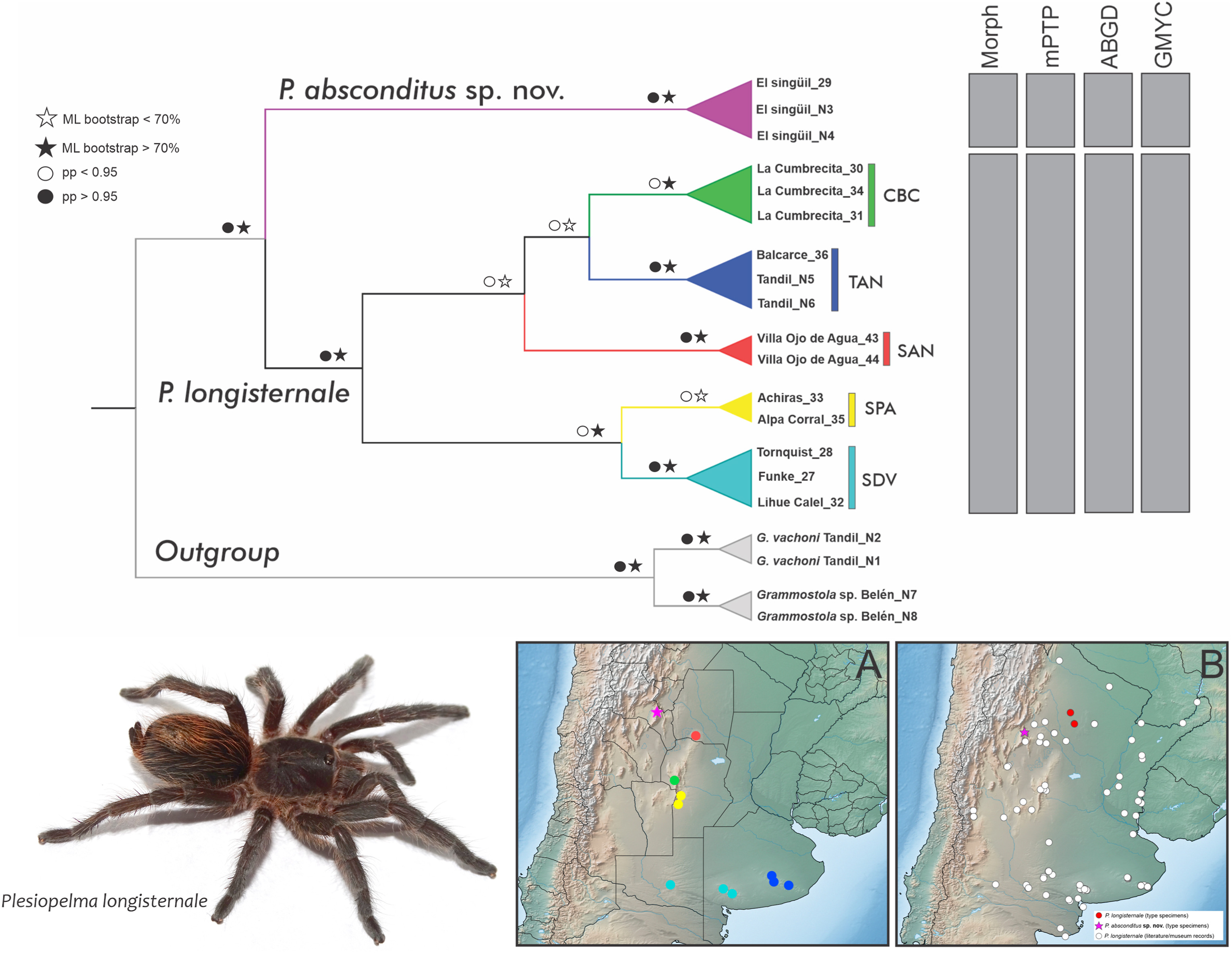
Plesiopelma longisternale is a widespread tarantula in Argentina and its limit is difficult to determine due to their morphological variation among populations. Males are distinguishable by the following character combination: a field of spines on the apical half of the palpal tibia, a very long embolus and a field of spines on the reotrolateral face of cymbium; females are characterized by long spiraled ducts distant from each other. Here, we used mitochondrial DNA (cox1) to reconstruct the first phylogeny of P. longisternale, in combination with morphological data and molecular species delimitation, to assess the taxonomic limits of this species. Our phylogenetic results confirm a close relationship among the populations from central Argentina and a new evolutionary independent lineage identified as a new species, Plesiopelma absconditus, which is here diagnose, described and illustrated. We further analyzed the diagnostic characters of P. longisternale through the examination of the types and specimens from many populations and found that their morphological intraspecific variations largely overlap. Altogether, our results demonstrate that some of the variability of P. longisternale in central Argentina represent polymorphisms of a single species supported by molecular data. In addition, we discovered a new species from this genus distinguishable by molecular and morphological data and highlight the need for multiple lines of evidence to solve the taxonomic problems in species of tarantulas.
Nelson, F., Micaela, N., & Daniela, S. (2023). An integrative taxonomy approach evaluates the limits of the widespread tarantula Plesiopelma longisternale (Araneae: Mygalomorphae: Theraphosidae) and reveals a new species from Argentina. Zoologischer Anzeiger. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcz.2023.12.003